RabbitMQ 中有 4 种不同的 Exchange ,分别是 Direct 、Topic 、Fanout 和 Headers 。
Direct
RabbitMQ 默认的 Exchange Type 。使用此方式 Exchange 会比较 RoutingKey 和 BindingKey ,两个相等才会将消息路由到 Queue ,如果没有和 RoutingKey 相等的 BindingKey ,消息就会被丢弃。
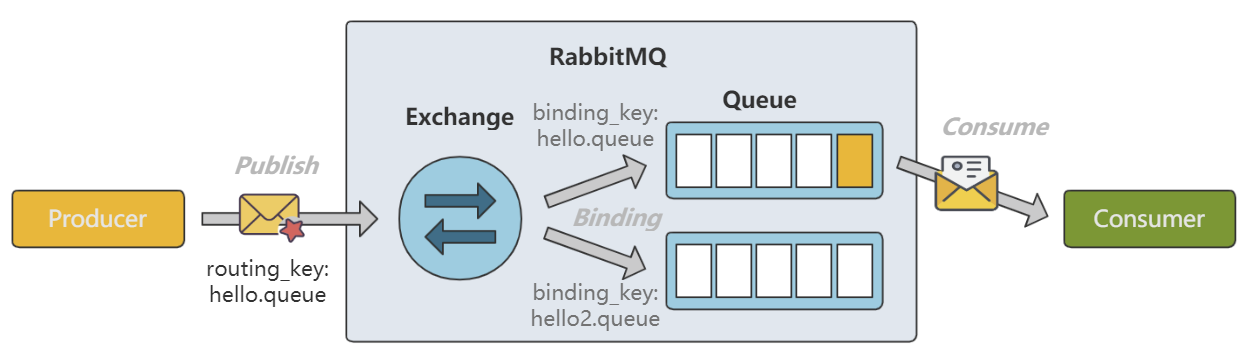
有两个 Queue 绑定到 Exchange ,分别是 hello.queue 和 hello2.queue 。Producer 向 Exchange 发送消息,RoutingKey 作为参数存放在消息的 header 。Exchange 会将消息路由到 hello.queue 的队列中,因为 RoutingKey 和 BindingKey 完全相等。
Topic
使用此方式 Exchange 会通过模式匹配的方式进行路由,RoutingKey 可以使用 “.” 、“#” 、“” ,例如 order.create. ,order.# ,”*“ 匹配 0 或 1 个,”#“ 匹配 0 或 n 个。Consumer 可以订阅任何感兴趣的 Topic ,Exchange 会将消息路由到所有符合模式的队列中。
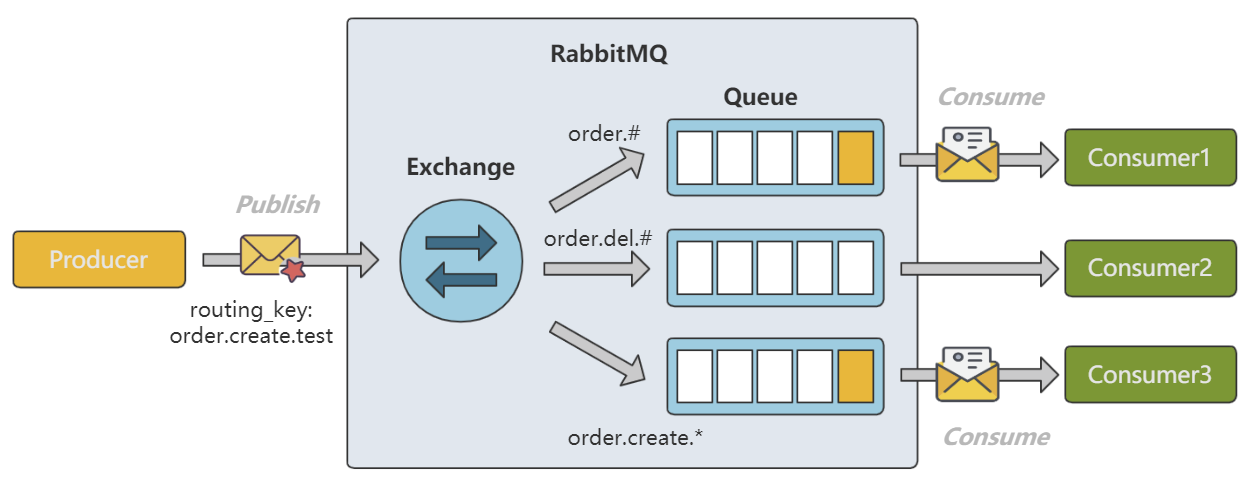
Consumer1 订阅了 order.# ,Consumer2 订阅了 order.del.# ,Consumer3 订阅了 order.create. 。Producer 向 Exchange 发送了一条消息,RoutingKey 为 order.create.test ,order.create. 、order.# 都可以匹配 order.create.test ,因此 Consumer1 和 Consumer3 都会收到消息, order.del.# 无法匹配,则 Consumer2 不会收到消息。
Fonout
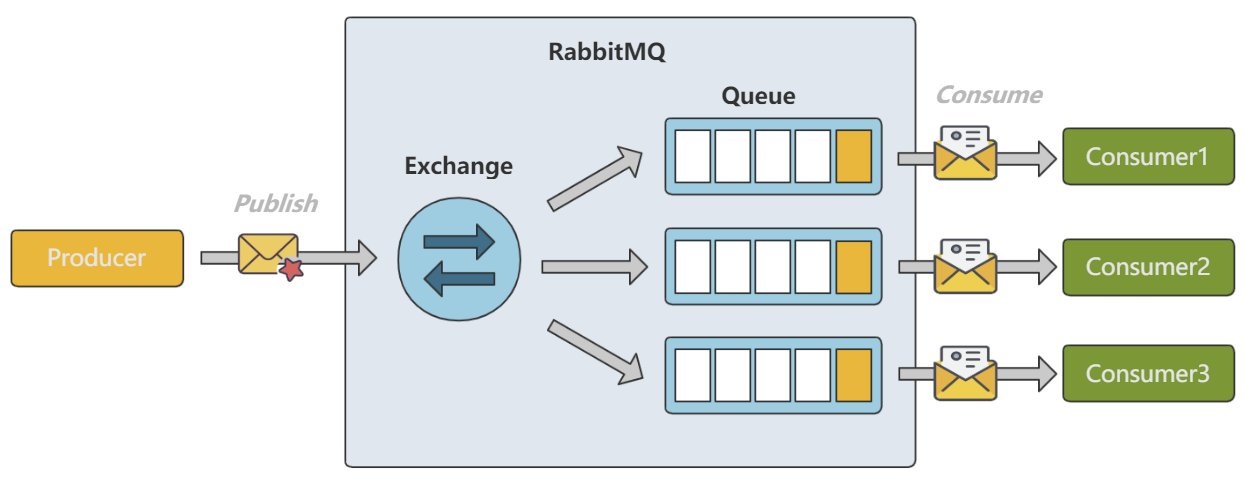
使用此方式 Exchange 会消息复制多份,并路由到所有与 Exchange 绑定的队列,此时将不再关心 RoutingKey 。这种模式通常在需要对相同的消息采取不同的处理时使用。
Headers
使用此方式 Exchange 在绑定 Queue 时会增加一个特殊参数 x-match ,x-match 有两个值,分别是 any 和 all ,默认是 all 。Exchange 在路由匹配时,通过消息的 Header 进行匹配,而不是 RoutingKey 。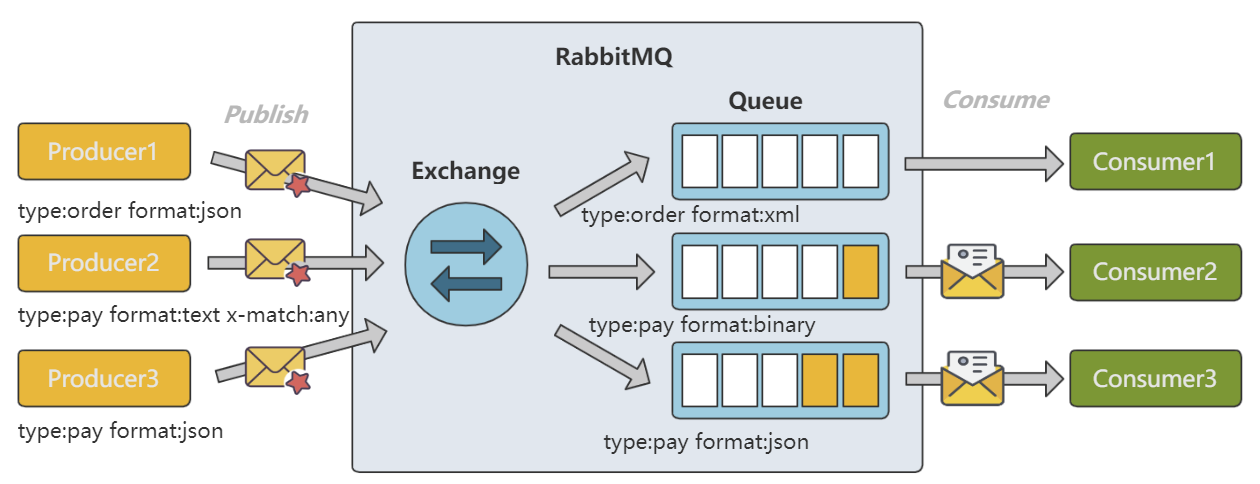
Consumer1 订阅了 type:order format:xml ,Consumer2 订阅了 type:pay format:binary ,Consumer3 订阅了 type:pay format:json 。Producer1 发送的消息 headers 为 type:order format:json ,Exchange 没有与其匹配的 Queue ,所以消息会被丢弃。Producer2 发送的消息 headers 为 type:pay format:text x-match:any ,Exchange 会将消息路由给 Queue2 和 Queue3 。Producer3 发送的消息 headers 为 type:pay format:json ,Exchange 会将消息路由到 Queue3 。
